The SysMain service does not critical processes within Windows 10. It is safe to stop it at anytime. So if you have issues with the disk performance because of SysMain / Superfetch, th you have 2 flavors: disable SysMain completely, or tune SysMain to reduce impact. Disable SysMain in Services. If you have svchost.exe high memory and CPU usage problem you will see that the amount of memory usage svchost.exe uses will keep increasing until CPU becomes 99 or 100%. Solutions for svchost.exe high memory usage. There are several solutions to this problem. Service host: local system continuous 100% disk usage I have a windows 10 64bit system.
- Service Host Taking Up Memory
- High Memory Usage Vista
- Service Host Sysmain High Memory Usage Tool
- Service Host Sysmain High Memory Usage In Task Manager
Superfetch is a finctionality in windows 10 introduced for two purposes. The first one is decreasing boot time and the second one is loading apps faster. Superfetch does this by preloading them in the memory. It also tracks your usage pattern for a better preloading decision. For example, if you open chrome in the morning, it will preload chrome in the morning hours, so that app load faster. But sometimes prefetch becomes a major cause of high disk usage. Here in this article, we will discuss how to disable superfetch in windows 10.
Note – In new Windows 10 Update, Windows OS have renamed it as SysMain. To disable this service through Registry Editor, do the following.
Disable Superfetch / SysMain through Service manager
1. Search Services in the Taskbar Search
2. Now, Choose Services.

3. Locate Sysmain.
4. Double click on Sysmain.
5. Now, Choose Startup Type as Disabled from the dropdown.
6. Click on Stop to stop the service.
7. Choose Apply.
Service Host Taking Up Memory
Disable superfetch / Sysmain through command prompt
Step 1 – Open command prompt as admin.
Step 2 – Write the command code given below and hit enter.
Note: – To enable it again, just run the command given below.
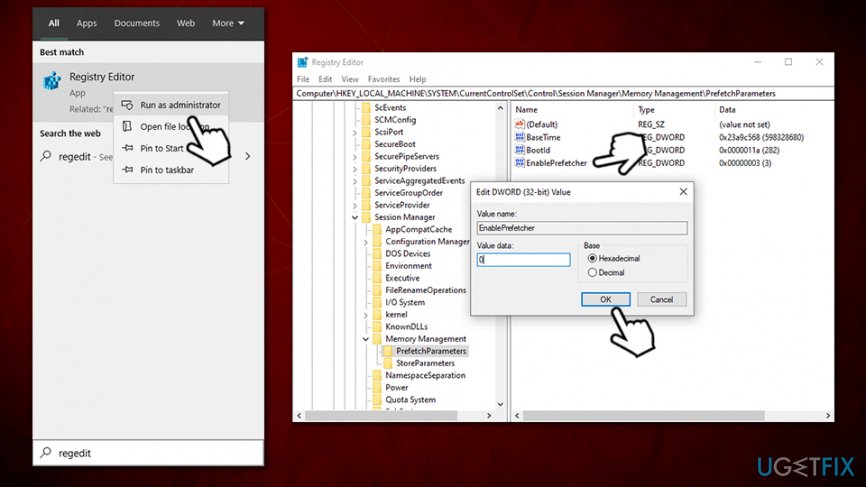
Disable superfetch through windows registry
Step 1 – Press Windows key + R together to bring up run command box.
Step 2 – Write Regeditin the run command box and hit enter.
Step 3 – Now browse to the location given below.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- SYSTEM
- CurrentControlSet
- Control
- Session Manager
- MemoryManagement
- PrefetchParameters
Step 4 – On the right side of the popped up box, find EnableSuperfetch entry from the list.
Put one of the following values in EnableSuperfetch depending upon your requirement.
0 – to disable Superfetch completely
1 – to enable prefetching when program is launched
2 – to enable boot prefetching
3 – to enable prefetching of everything
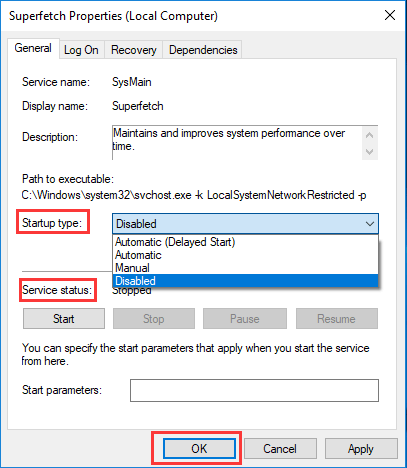
If this entry is absent, just do a right-click the on the PrefetchParametersfolder, then choose New > DWORD Value. Name this EnableSuperfetch and do the steps given above.
Saurav is associated with IT industry and computers for more than a decade and is writing on The Geek Page on topics revolving on windows 10 and softwares.
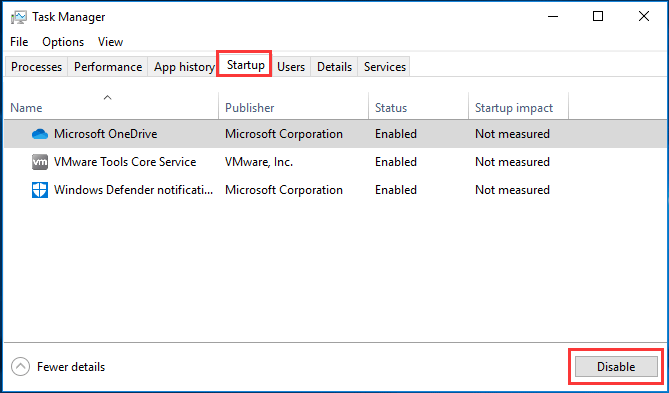
Service Host: Local System (Network Restricted) Is Using Too Much Of Your CPU Resources
Some time ago Microsoft started changing the Windows functionality from depending on internal Windows services (which ran from .exe files) to using .dll files. You can’t launch a .dll file directly from Windows the same way you can launch an executable (.exe) file. Instead, a shell that is loaded from a executable file is used to host these .dll services. And that is how the Service Host process (svchost.exe) was invented.
Service Host: Local System is a collection of system processes which operates automatically through system. It includes processes like Windows Auto Update and many others which takes up huge memory, disk, RAM etc. You may have noticed that almost all your available network is taken by these processes. This problem is frequent in Windows 8 and 10 operating systems. So, Service Host(svchost.exe) is a generic service hosting container, any number of required system services can be running in it. Running services are arranged into groups that are all somehow related, and then a single Service Host instance is created to host each group.
If you’re using Windows 8 or 10, processes are shown on the Processes tab in the Task Manager window by their full names. If a process serves as a host for multiple services, you can see all of these services by simply expanding the process group. By doing so you can very easily identify which services belong to each of the Service Host process.
Problems with high CPU (Central Processing Unit) usage can impact your PC performance remarkably. If you are running Windows 10 and you find that Service Host: Local System (Network Restricted) is taking much of your CPU, Disk or Memory usage then you are at the right place. In this article we are going to show you several ways how you can fix this problem. Read the guide below and find the solution which works best for you.
Table of Contents:
It is recommended to run a free scan with Malwarebytes - a tool to detect malware and fix computer errors. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections and eliminate computer errors. Free trial available.
Disable Superfetch
Superfetch is a Windows service that is intended to speed up application launching and improve system responsiveness. It caches data so that it can be immediately available to your application. Superfetch doest it by preloading programs you frequently use into RAM so that they do not have to be called from the hard drive. Sometimes this can affect the performance and to slow down your computer. This service may be the cause of high CPU usage and if this service is decreasing your computer’s speed, we recommended you to turn it off.
To disable Superfetch open Run dialog box. To open it type 'run' in Search and click on the 'Run' result. Or you can use Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open it. In opened Run dialog box type 'services.msc' and press Enter on your keyboard or click 'OK'.
In the opened Services window you will see a list of local services. Scroll down to find 'Superfetch' and right-click on it. Select 'Stop' from the dropdown menu to stop Superfetch service. Restart your computer for changes to take effect.
After disabling Superfetch service and restarting your computer the CPU usage should get back to normal.
End HP Processes
This one includes ending unnecessary HP (Hewlett-Packard) processes. You will need to use Task Manager for that. Task manager is a system monitor program used to provide information about the processes and programs running on a computer, as well as the general status of the computer. Some implementations can also be used to terminate processes and programs, as well as change processes priorities. To open Task Manager, press Ctrl + Alt + Delete on your keyboard or right-click on the Start menu and select 'Task Manager'.
Find (unnecessary) running HP processes and then turn them off by right-clicking on any of the processes and selecting 'End task' from the dropdown menu. Or select the HP process and then click on 'End task' in the bottom-right corner.
If this method helped to fix this problem with high CPU usage then you may need to repeatedly end those processes when this problem occurs the next time.
Troubleshoot Windows Update
Windows Update is a free Microsoft service for the Windows operating system, which automates downloading and installing software updates over the Internet. The service delivers software updates for Windows, service packs, patches, as well as the various Microsoft antivirus products (like Windows Defender) and driver updates for various hardware devices. Windows Update is a necessary part of running on any Windows operating system. On most computers with Windows operating system updates are installed automatically. However, it also can be the cause for high CPU usage. Try to run the Windows Update troubleshooter to see if there is a problem with it. Go to Control Panel and then select to view by small icons in the top-right corner. Click on 'Troubleshooting'.
In Troubleshooting window find 'View all' on the left pane and click on it.
Now you will see a list of computer problems that you can troubleshoot. Find 'Windows Update' (It should be the last one on the list) and right-click on it, select 'Run as administrator' from the dropdown menu.

In opened Windows Update window click on 'Advanced' and check the 'Apply repairs automatically' checkbox. Click 'Next' and follow the instructions on the screen to complete the troubleshooter.
Run SFC And DISM Scan
System File Checker is a utility in Windows that allows users to scan for corruptions in Windows system files and restore corrupted files. This guide describes how to run the System File Checker tool (SFC.exe) to scan your system files and to repair missing or corrupted system files. If a Windows Resource Protection (WRP) file is missing or is corrupted, Windows may not behave as expected. For example, some Windows functions may not work, or Windows may crash. The 'sfc scannow' option is one of the several specific switches available in the sfc command, the Command Prompt command used to run System File Checker. To run it you need to open Command Propmt first. To open it type 'command prompt' in Search and then right-click on the 'Command Prompt', select 'Run as administrator' from the dropdown menu to run Command Prompt with administrator privileges. You must run an elevated Command Prompt in order to be able to perform SFC scan.
In opened Command Prompt window type 'sfc /scannow' and press Enter on your keyboard to execute this command. System File Checker will start and it should take some time to complete the scan. It should take about 15 minutes. Wait for the scanning process to complete and then restart your computer.
If the SFC scan did not helped to fix the problem (or you could not run SFC scan) then try running the DISM scan as well. DISM stands for Deployment Image Servicing and Management and it can be used to repair and prepare Windows images, including the Windows Recovery Environment, Windows Setup, and Windows PE. To run DISM scan you need to open Command Prompt as administrator again and to type in this command: 'DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth'. Press Enter on your keyboard to execute it.
When DISM scan is finished, check if the problem still persists. If this did not helped, then try running SFC scan again if you could not run it the first time.
Fix The Memory Leak Using Registry Editor
Windows Registry, usually referred to as just the registry, is a collection of databases of configuration settings in Microsoft Windows operating systems. It is used to store much of the information and settings for software programs, hardware devices, user preferences, operating system configurations, and much more. Many of the options exposed in the registry are not accessible elsewhere in Windows. A wide variety of advanced settings can only be changed by directly editing the registry. Some other settings may be accessible through Group Policy – but the Group Policy editor is only included on Professional editions of Windows. The registry allows you to change most settings that can be accessed through Group Policy.
Note: Editing the registry is risky, and it can cause irreversible damage to your installation if you do not do it correctly.
Open the Run dialog box by typing 'run' in Search and click the 'Run' result.
In Run dialog box type 'regedit' and click 'OK' to open Registry Editor.
In opened Registry Editor follow this path: 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMControlSet001ServicesNdu'. Once you clicked on 'Ndu', double-click the 'Start' on the right pane.
Change 'Value data:' to 4 and click 'OK'. Changing its value will plug the memory leak in the non-paged pool. Close registry editor and restart your computer to see if this helped, and System Host: Local System (Network Restricted) is no longer using too much of your CPU (or Disk).
End SCVhost Process
Ending the Service Host process in the Task Manager might solve this issue as well. To open Task Manager, press Ctrl + Alt + Delete on your keyboard or right-click on the Start menu and select 'Task Manager'. In opened Task Manager window click on 'More details' to expand it and you will see all the running processes. Find the process named “Service Host: Local System”. There could be several processes named like this so find the one which hosts 'Windows Update' and the 'Update Orchestrator Service'. Select these processes and click 'End task' or right-click on the processes one by one and select 'Stop' from the dropdown menu.
Perform Clean Boot
When you start Windows by using a normal startup operation, several applications and services start automatically, and then run in the background. These programs include basic system processes, antivirus software, system utility applications, and other software that has been previously installed. These applications and services can cause software conflicts. A clean boot is performed to start Windows by using a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This helps eliminate software conflicts that occur when you install a program or an update or when you run a program in Windows. To perform a clean boot, type 'system configuration' in Search and click on the 'System Configuration' result.
In opened System Configuration window click on the 'Services' tab and then mark the 'Hide all Microsoft services' checkbox. Then click on 'Disable all'.
Then click on 'Startup' tab and click on 'Open Task Manager'.
Under Task Manager's Startup tab select the first application and click 'Disable' to disable it, disable all applications one by one repeating this step. Once you disabled all programs close Task Manager and click 'OK' in the System Configuration's Startup tab and restart your computer to see if this helped to fix the issue.
Your computer will run only with with default applications and services. If this helped then it means that one of the disabled applications is causing the error. To find that application you need to repeat the steps mentioned above, enable startup services and enable applications one by one until you find it. You need to restart your computer after enabling the application or service to apply changes. Once you find the problematic application you can keep it disabled, update it, reinstall it or totally remove it from your Windows operating system.
Restart Windows Update Service
High Memory Usage Vista
This is the last method you might want to try out, you will need to restart Windows Update service using Command Prompt and its commands. To open Command Prompt type 'command prompt' in Search and then right-click on the 'Command Prompt', select 'Run as administrator' from the dropdown menu to run Command Prompt with administrator privileges.
In opened Command Prompt window type 'net stop wuauserv' and press Enter on your keyboard, then type 'net stop bits' and press Enter on your keyboard again to execute these commands.
Service Host Sysmain High Memory Usage Tool
Minimize Command Prompt window (do not close it) and go to File Explorer and follow this path: 'Windows > SoftwareDistribution'. Delete all files that are on the SoftwareDistribution folder.
No go back to Command Prompt window and type in these commands: 'net start wuauserv' and 'net start bits'. Press Enter on your keyboard after entering each command.
Thats all we have for now. We hope that at least one of the methods helped you to reduce the CPU or Disk usage for 'Service Host: Local System (Network Restricted)' services and you can now normally use your computer without any problems.